How (and why) to roll back Windows updates on your PC
Why Roll Back Windows Updates?
Windows updates aim to improve performance and security. But occasionally, they introduce problems like:
- Software incompatibility.
- System instability.
- Driver conflicts.
- Decreased performance.
Rolling back updates helps resolve these issues quickly. It restores your PC to a stable state.
Before You Begin
Check Update Details
Find out which update caused the problem:
- Open Settings > Update & Security.
- Click View update history.
- Note the KB (Knowledge Base) number of the recent update.
Backup Your Data
Before rolling back, back up your files. This ensures you don’t lose important data during the process.
How to Roll Back Windows Updates
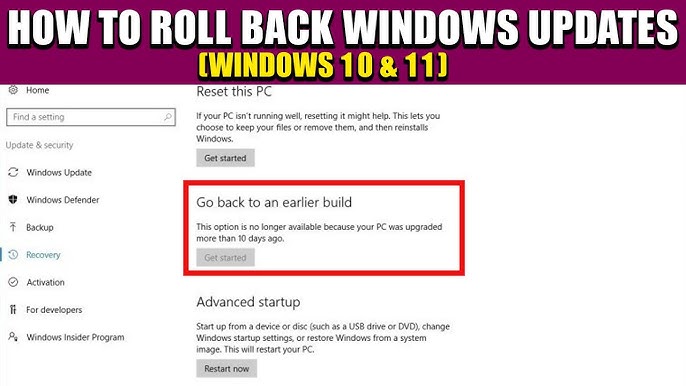
Method 1: Use Settings
This is the easiest method for recent updates:
- Open Settings > Update & Security.
- Select Recovery.
- Click Go back to the previous version of Windows 10/11.
- Follow on-screen instructions.
Method 2: Uninstall Updates
For individual updates, follow these steps:
- Open Settings > Update & Security.
- Select View update history.
- Click Uninstall updates.
- Locate the problematic update.
- Right-click and choose Uninstall.
Method 3: Use Advanced Startup
If your system won’t boot, try Advanced Startup:
- Restart your PC and press F8 during startup.
- Choose Troubleshoot > Advanced options.
- Select Uninstall Updates.
- Follow the prompts to roll back updates.
Method 4: System Restore
System Restore rolls back both updates and settings:
- Search for System Restore in the Start menu.
- Select Create a restore point.
- Click System Restore.
- Choose a restore point before the update.
- Follow on-screen instructions.
After Rolling Back Updates
Pause Automatic Updates
To prevent the issue from recurring:
- Open Settings > Update & Security.
- Select Advanced options.
- Enable Pause updates for a set period.
Report Issues to Microsoft
Inform Microsoft of the problem. This helps them fix the update in future releases.
Benefits of Rolling Back Updates
Improved Stability
Rolling back removes faulty updates, restoring system stability.
Better Performance
Undoing problematic updates improves performance.
Compatibility Fixes
Removing updates resolves software and hardware conflicts.
Potential Risks of Rolling Back Updates
Security Vulnerabilities
Rolling back updates may leave your system exposed to threats.
Lost Features
You might lose new features introduced in the update.

Tips to Avoid Update Issues
Enable Update Notifications
Stay informed about updates before they install.
Check Compatibility
Verify compatibility with critical software or hardware.
Keep Drivers Updated
Outdated drivers often cause issues after updates.
Alternatives to Rolling Back Updates
Update Troubleshooter
Use Microsoft’s built-in troubleshooter to fix update issues.
Manually Reinstall Drivers
If drivers cause problems, update or reinstall them manually.
Wait for Patches
Microsoft usually releases patches for faulty updates.
Conclusion
Rolling back Windows updates on your PC is essential for resolving issues. Whether you face performance drops or compatibility problems, this guide ensures a smooth rollback process. Always prioritize data backup and system stability when managing updates.




