Understanding Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAO)
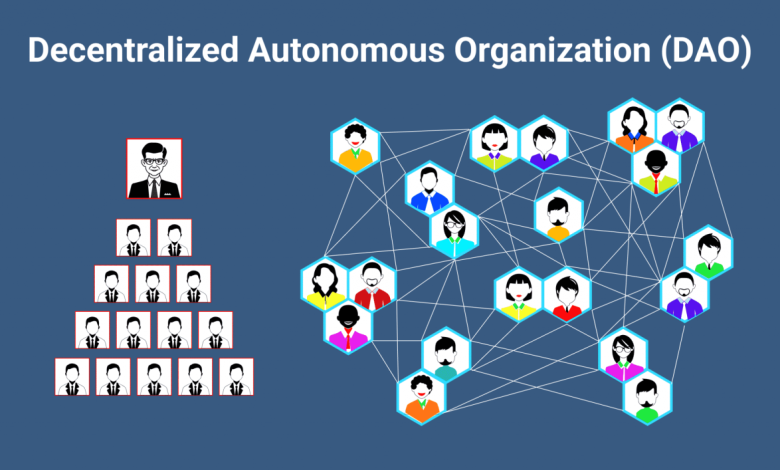
What is a Decentralized Autonomous Organization?
A Decentralized Autonomous Organization, or DAO, is an organization that operates on the blockchain. It’s governed by smart contracts, which are self-executing agreements coded into the blockchain. These contracts determine the rules and actions of the DAO, ensuring transparency and security.
A DAO’s structure is unique. It has no central authority or traditional leadership. Instead, it is managed collectively by its members. Decisions are made through a voting system, where each member has a say in the organization’s direction. This approach offers a democratic process, allowing participants to control the DAO directly.
How Does a DAO Work?
A DAO relies on smart contracts to manage its operations. These contracts contain the rules and guidelines that dictate the DAO’s actions. Once set up, the DAO operates autonomously, executing functions based on these contracts. For instance, if a DAO’s contract specifies a voting requirement to approve funding, the DAO will automatically enforce it.
The process begins with a group of people or developers creating a set of smart contracts. These contracts establish the DAO’s purpose and rules. After that, the organization is deployed on the blockchain, and it becomes self-sustaining. Members join by purchasing tokens or contributing resources. These tokens often represent voting power, allowing members to participate in decision-making.
Voting takes place on the blockchain. Each vote is transparent and secure, allowing all members to see the results. This transparency builds trust and removes the need for a central authority. By placing control in the hands of the community, DAOs provide a new approach to governance.
1. Key Benefits of DAOs
DAOs offer several advantages that appeal to modern organizations and communities:
- Transparency: Blockchain technology ensures that all transactions and votes are visible to members. This transparency prevents manipulation and builds trust.
- Decentralization: DAOs distribute power among all members, eliminating the need for a central authority. This structure fosters fairness and inclusivity.
- Efficiency: Smart contracts automate many functions, reducing the time and costs associated with traditional management.
- Global Access: Anyone with internet access can join a DAO. This global reach enables DAOs to bring together people from diverse backgrounds.
These benefits make DAOs attractive to organizations seeking more transparency, inclusivity, and efficiency. By removing central control, DAOs create a level playing field where every member has a voice.
2. Examples of Successful DAOs
Several DAOs have already gained popularity and demonstrated the potential of decentralized governance. Here are a few examples:
- MakerDAO: MakerDAO is a well-known DAO in the world of finance. It manages the DAI stablecoin, which is pegged to the US dollar. Through voting, MakerDAO members make decisions about the platform, including interest rates and risk parameters.
- Uniswap: Uniswap, a decentralized exchange, operates through a DAO. Token holders make decisions on updates, fee structures, and other aspects of the exchange.
- The DAO (2016): Although it ultimately failed due to a hack, The DAO was one of the first DAOs and highlighted the potential for this technology. The hack led to improved security practices, helping future DAOs to be more resilient.
These DAOs showcase how decentralized governance can operate in various fields, from finance to technology. They serve as examples of how DAOs can function, offering inspiration for new projects.
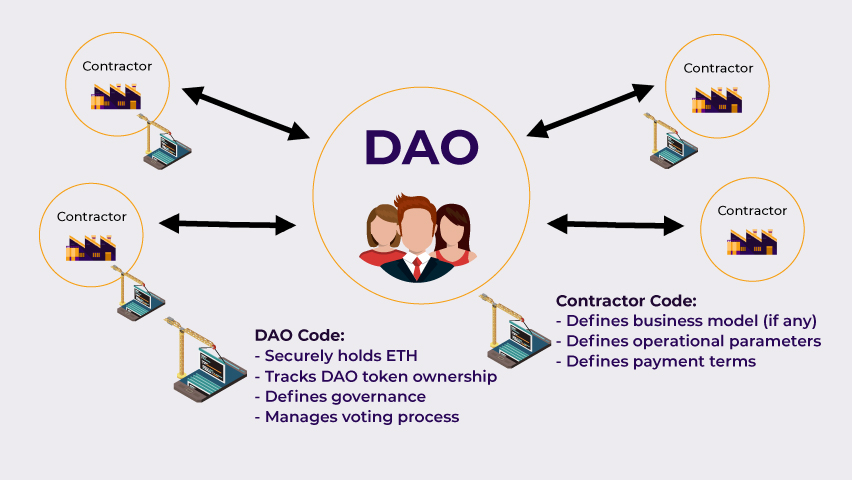
3. How DAOs are Transforming Governance
DAOs are reshaping governance by offering a more democratic approach to decision-making. Unlike traditional organizations with hierarchical leadership, DAOs rely on collective voting. Each member has voting rights, often tied to their token holdings, and decisions reflect the community’s will.
In traditional organizations, leaders make decisions that may not align with all members’ interests. In contrast, DAOs distribute authority evenly. This setup fosters a sense of ownership and community. Members feel more invested in the organization’s success, as they play an active role in its direction.
This governance model also offers more flexibility. DAOs can quickly adapt to changing circumstances. If members want to change a rule, they can propose and vote on it, updating the DAO’s structure without complex processes. This adaptability is particularly valuable in fast-evolving industries like technology and finance.
4. Challenges Facing DAOs
Despite their benefits, DAOs face challenges that need addressing:
- Security Risks: Smart contracts can be vulnerable to hacking. The infamous DAO hack in 2016, which led to the loss of millions, highlighted this risk. Improving contract security is essential for DAOs to gain widespread trust.
- Legal Uncertainty: Many countries lack clear regulations for DAOs. Without legal frameworks, DAOs may face challenges regarding liability, taxes, and compliance.
- Scalability: As DAOs grow, managing thousands of members can become complex. Ensuring efficient voting and decision-making at scale is a challenge that developers need to address.
- Decision Paralysis: Voting-based governance can lead to decision paralysis if members cannot reach a consensus. This issue can slow down decision-making and hinder progress.
These challenges are significant but not insurmountable. Developers and communities are actively working to address these issues, improving the resilience and functionality of DAOs.
5. DAOs and the Future of Work
DAOs could redefine the future of work by offering new ways to organize teams and projects. In a DAO, people can collaborate without traditional employment structures. Contributors receive tokens, which may represent voting power or financial rewards. This model offers flexibility and empowers individuals to choose projects based on their skills and interests.
Moreover, DAOs remove the need for a central office or management structure. This setup aligns with the growing trend of remote work, allowing people from around the world to participate. DAOs create opportunities for individuals to work autonomously, contributing to projects they are passionate about.
6. Applications of DAOs Beyond Business
The applications of DAOs extend beyond business. They can be used for charitable organizations, social movements, and community groups. For instance, a DAO could pool resources for disaster relief, with members voting on how to allocate funds. This approach offers transparency, as every member can see where donations are directed.
Similarly, DAOs can support creative projects, such as funding art or music collectives. By pooling resources and managing projects collectively, DAOs give artists and creators a new way to collaborate and finance their work. This model opens doors to diverse applications, making DAOs versatile tools for various purposes.
7. Legal and Ethical Considerations for DAOs
DAOs operate in a legal gray area. Since they lack a central authority, liability and accountability can be ambiguous. For instance, if a DAO faces legal action, identifying responsible parties can be challenging. Clarifying legal frameworks for DAOs is essential for their long-term success.
Ethically, DAOs raise questions about decision-making. Since voting power often correlates with token holdings, wealthier members may have more influence. Ensuring fairness and inclusivity in decision-making requires careful planning.
Addressing these legal and ethical concerns is crucial for DAOs to gain legitimacy and acceptance in mainstream society. Clear guidelines and regulations will help DAOs operate more effectively and responsibly.
8. The Potential Future of DAOs
The future of DAOs looks promising. As blockchain technology evolves, DAOs will likely become more secure, efficient, and adaptable. With clearer regulations and improved smart contract security, DAOs could become a popular model for organizations worldwide.
We may also see more hybrid models, combining DAOs with traditional organizational structures. This approach could offer the benefits of decentralization while addressing some challenges, like legal compliance and accountability.
As interest in DAOs grows, more industries may explore their potential. From finance to social causes, DAOs offer a new way to organize and manage resources. With further development, DAOs could play a significant role in the future of business and governance.
Conclusion
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) are reshaping how we think about governance, work, and collaboration. By using blockchain technology, DAOs provide transparency, efficiency, and global accessibility. They offer a democratic approach to decision-making, allowing members to control the organization collectively.
However, DAOs also face challenges, including security risks, legal uncertainties, and scalability issues. Addressing these challenges is essential for DAOs to thrive and achieve their full potential.
DAOs represent a promising future for organizations. As they continue to evolve, they could become a significant force in both the business and social sectors. Understanding DAOs helps us glimpse into the future of decentralized governance.