What is a Phishing Scam?

What is a Phishing Scam?
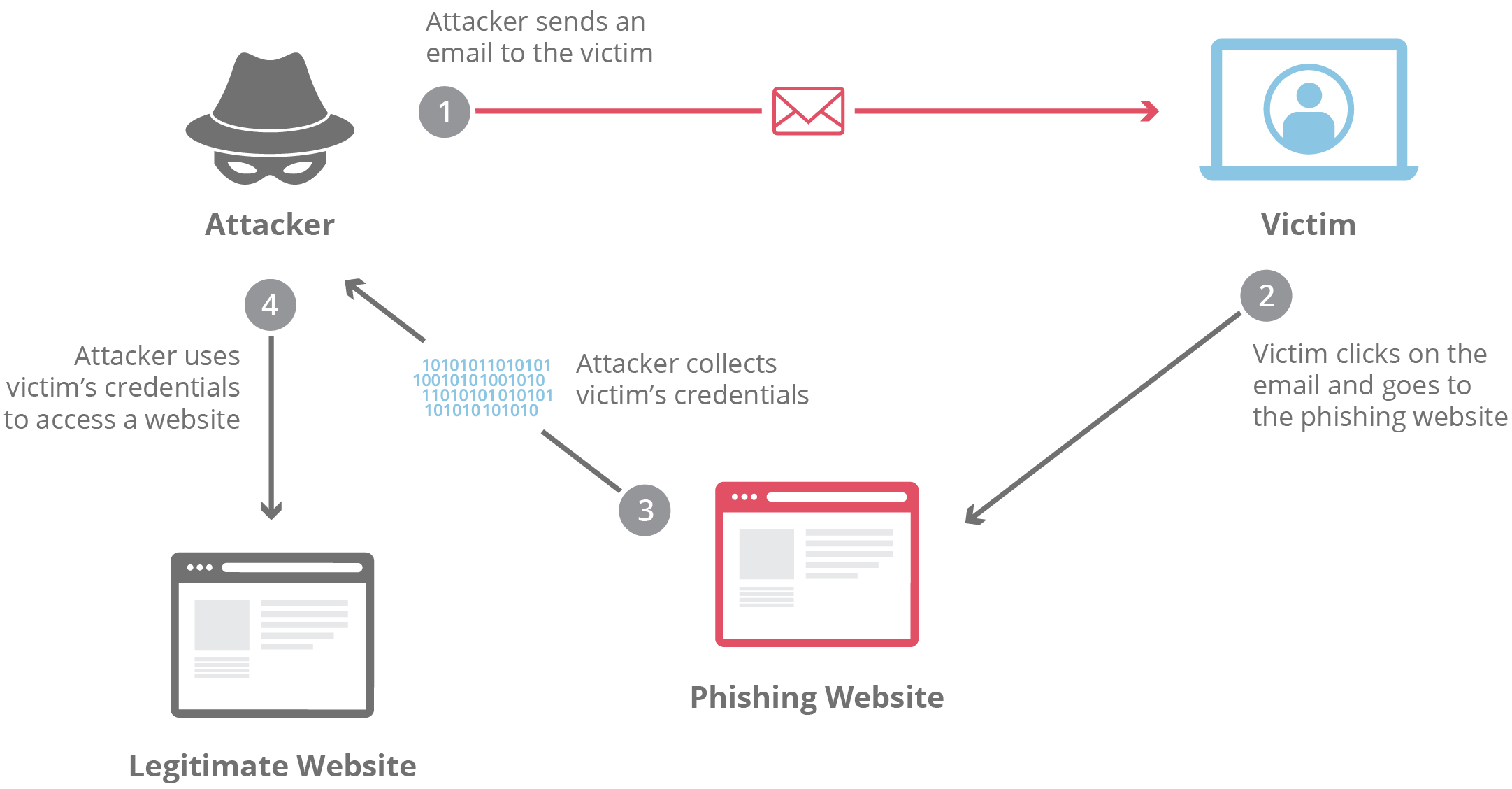
Phishing is a type of cyber attack that aims to trick people into revealing sensitive information. It usually involves fake emails, messages, or websites that look legitimate but are created by cybercriminals. They try to steal passwords, credit card numbers, or personal details. With phishing attacks on the rise, it’s crucial to know how to spot these scams. Protecting yourself from phishing can prevent identity theft, financial loss, and data breaches.
Common Types of Phishing Scams
There are several types of phishing scams. Knowing the different forms can help you recognize a scam more easily.
- Email Phishing: This is the most common type. Attackers send fake emails pretending to be from reputable companies or contacts. They often contain links or attachments that lead to malicious sites.
- Spear Phishing: These attacks are more targeted. Cybercriminals research their victims and personalize messages to increase their chances of success. Spear phishing often targets specific individuals or departments within an organization.
- Smishing and Vishing: Smishing uses SMS messages, while vishing uses phone calls. Attackers may pretend to be from banks, tech support, or government agencies to gain your trust.
- Clone Phishing: In this type, attackers clone a legitimate email you’ve received before. They change the links or attachments to lead to a malicious site or file.
- Pharming: This involves redirecting a legitimate website’s traffic to a fake site. Victims may not realize they’re on a malicious site because it looks identical to the real one.
By recognizing these different types, you can be more alert to suspicious messages and calls.

Key Signs of a Phishing Scam
Phishing scams often have specific characteristics that make them recognizable. Here’s what to look for:
1. Suspicious Sender Address
One of the first clues is the sender’s email address. Phishing emails often come from addresses that look similar to official ones but contain slight variations. For example, an attacker may use “@yourbаnk.com” instead of “@yourbank.com.” Look closely at the sender’s domain name. If it seems unusual or has extra characters, it could be a phishing attempt.
2. Urgent Language and Scare Tactics
Phishing emails often use urgent language to make you act quickly. They may say things like “Your account will be suspended” or “Immediate action required.” Scare tactics are used to create panic, making you more likely to click on links without thinking. Legitimate companies rarely use this approach. Always pause and consider whether the request seems reasonable.
3. Generic Greetings
Phishing emails often use generic greetings like “Dear Customer” or “Dear User.” Reputable companies, especially banks or service providers, usually address you by name. If you receive an email with a vague greeting, be cautious.
4. Poor Grammar and Spelling Errors
Professional emails from legitimate companies are usually free of grammar and spelling mistakes. Phishing emails, on the other hand, often contain errors. Attackers may use translation tools or rush to create the email, resulting in poor quality. If the message looks unprofessional or contains obvious mistakes, it could be a scam.
5. Suspicious Links and Attachments
Phishing emails often contain links or attachments designed to trick you. Hover over any links (without clicking) to see the actual URL. If it doesn’t match the company’s website or looks strange, it’s likely a phishing link. Attachments, especially from unknown senders, should also raise suspicion. Malware or ransomware can be hidden in attachments, so avoid downloading them.
6. Requests for Personal or Financial Information
Legitimate companies rarely ask for sensitive information over email. If an email requests your password, credit card number, or Social Security number, it’s probably a scam. Banks and service providers know that email isn’t a secure way to collect this information. Be cautious if you receive any message asking for personal details.
7. Unusual Requests or Instructions
Some phishing scams may ask you to perform unusual tasks, like making a payment to a strange account or changing account settings. Always question these types of requests. If you’re unsure, contact the company through their official channels before taking any action.
Real-Life Examples of Phishing Scams
Examining real-life phishing examples can help you recognize warning signs. Here are a few common examples:
- Fake Bank Alerts: These emails claim to be from your bank, warning you of suspicious activity. They may ask you to click a link to “verify your account.” The link leads to a fake website that looks like your bank’s, where attackers capture your login details.
- Package Delivery Scams: With online shopping on the rise, scammers use fake delivery notices. They claim there’s an issue with your shipment and provide a link for tracking. The link leads to a fake site designed to steal information or install malware.
- Tech Support Scams: Attackers impersonate tech support from companies like Microsoft. They may say your computer has a virus and ask for remote access. They then attempt to steal data or demand payment for “fixing” your device.
These examples highlight the various tactics scammers use to deceive people. Staying alert to these types of scams is crucial.
What to Do If You Suspect a Phishing Scam
If you receive a suspicious message, here’s how to handle it:
- Don’t Click Any Links or Download Attachments: Avoid clicking on any links or opening attachments from unknown sources. These could lead to malicious websites or install harmful software on your device.
- Verify the Sender: If the email appears to be from a trusted company, contact them directly. Use official contact information from the company’s website, not the information in the email. This helps confirm if the message is legitimate.
- Report the Scam: Most companies and email providers have options for reporting phishing. Reporting scams helps prevent others from falling victim. You can also report phishing attempts to cybersecurity organizations or government agencies.
- Delete the Email or Message: Once you’ve confirmed the message is fake, delete it immediately. Avoid responding or engaging with the sender in any way.
- Update Your Security Software: Ensure your antivirus and other security software are up to date. These tools can detect and block phishing attempts.
Tips to Protect Yourself from Phishing Scams
Phishing is constantly evolving, but there are ways to protect yourself. Here are some tips:
- Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security to your accounts. Even if someone gets your password, they’ll need a second verification method, like a code sent to your phone.
- Regularly Change Passwords: Strong, unique passwords reduce the risk of unauthorized access. Changing passwords regularly adds another layer of protection.
- Educate Yourself and Others: Staying informed about phishing tactics helps you recognize scams. Share your knowledge with friends, family, and colleagues to create a safer environment for everyone.
- Be Cautious with Public Wi-Fi: Avoid accessing sensitive accounts on public Wi-Fi networks. Public networks are less secure, making it easier for hackers to intercept data.
- Install Anti-Phishing Software: Many security programs offer anti-phishing features. These tools can identify fake websites, emails, and other phishing attempts, providing an additional line of defense.
The Future of Phishing Scams
Phishing tactics continue to evolve. Cybercriminals are using more advanced methods, including AI-generated content, to make phishing emails more convincing. As technology advances, it’s likely that phishing scams will become harder to detect. However, staying informed and cautious will help you protect yourself from these evolving threats.
Organizations and individuals need to be proactive. Implementing cybersecurity training, using anti-phishing software, and spreading awareness can reduce the risk of falling victim to phishing scams. By staying vigilant, you can recognize the signs of phishing and keep your information safe.
Conclusion: Stay Alert and Protect Yourself
Phishing scams are a serious threat in today’s digital world. Recognizing the signs and staying cautious are the best ways to protect yourself. By following these tips, you can reduce the risk of becoming a phishing victim. Always think before you click, question unusual requests, and report suspicious messages. Cyber awareness is the key to a safer online experience.