What is Edge Computing?

What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is an innovative approach to data processing that brings computation and data storage closer to where it is needed. This decentralization allows for faster data processing, reduced latency, and improved performance, particularly for applications that require real-time analysis. As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand, this technology has become essential for managing the vast amounts of data generated by connected devices.
This article explores the fundamentals of edge computing, its benefits, various applications, and the challenges it faces.
Understanding Edge Computing
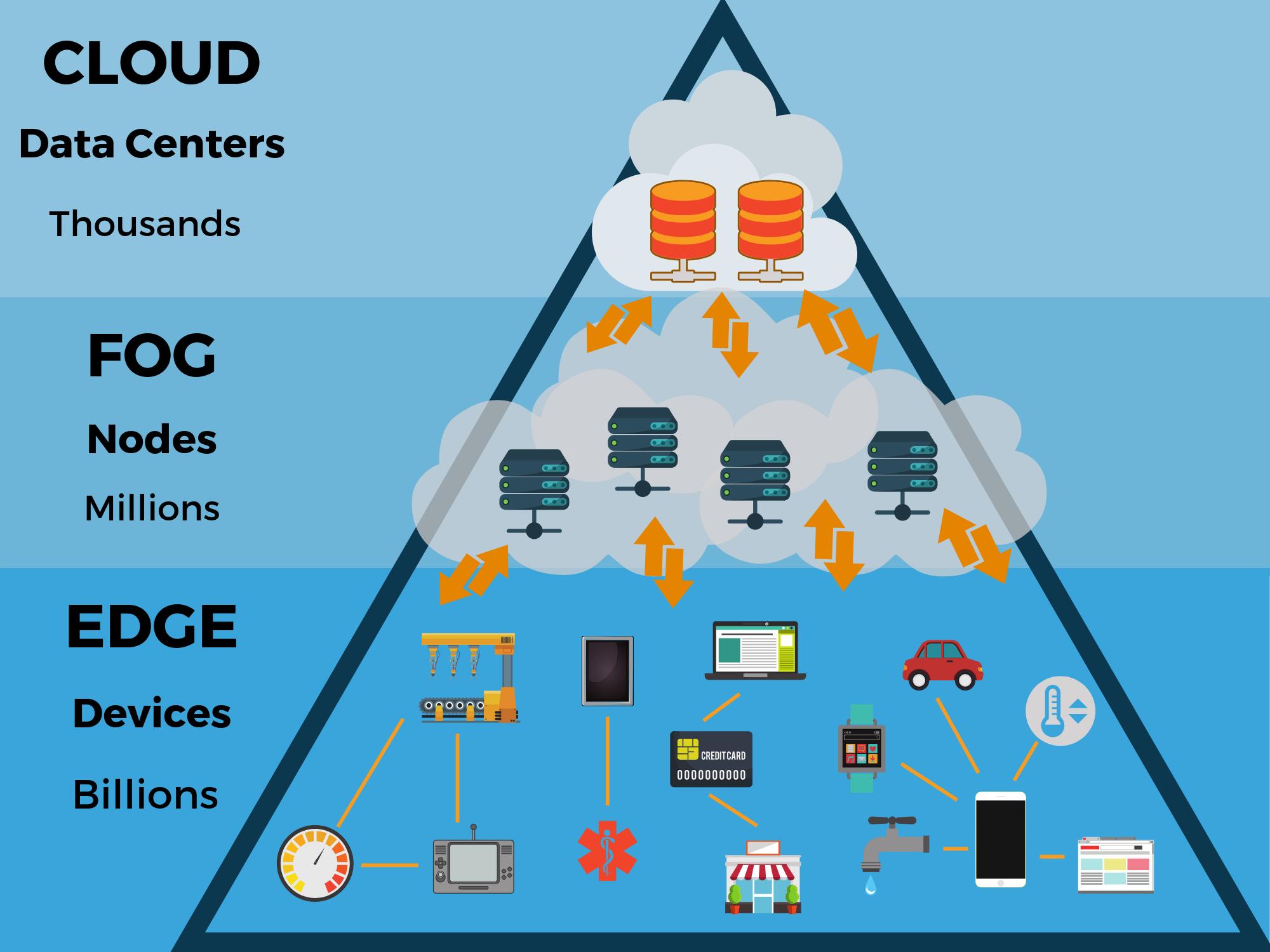
At its core, this technology operates by placing computing resources closer to the data source. Here are its key components:
- Devices – These IoT devices or sensors collect data from their environment. Examples include smart cameras and industrial sensors, which gather information for processing.
- Gateways – Gateways serve as intermediaries between edge devices and central data centers. They aggregate data from multiple sources, perform initial processing, and send relevant data to the cloud for further analysis.
- Local Processing – By handling data close to its origin, organizations can analyze information in real time. For instance, a manufacturing facility can monitor equipment performance and detect issues proactively.
- Centralized Data Centers – Although edge computing reduces reliance on centralized systems, they still play a vital role. Central servers handle larger data processing tasks and long-term storage.
Benefits of Decentralized Processing
The shift to edge computing offers numerous advantages:
- Reduced Latency – Processing data closer to its source significantly decreases the time it takes for information to travel to and from the cloud. This is crucial for applications that require immediate responses, like autonomous vehicles or remote monitoring.
- Bandwidth Efficiency – By minimizing the amount of data sent to the cloud, organizations can reduce bandwidth usage. This is particularly beneficial in environments with limited connectivity, allowing for more efficient network resource utilization.
- Enhanced Security – Keeping sensitive data closer to its origin reduces the risk of exposure during transmission. Local processing enables immediate responses to security threats, improving overall data protection.
- Increased Reliability – Edge systems can continue to operate even if connectivity to the central cloud is interrupted. This resilience is essential for critical applications in healthcare, manufacturing, and transportation.
- Cost Savings – By minimizing data sent to the cloud, businesses can lower storage and processing costs. Additionally, faster data processing can lead to increased operational efficiency and further cost reductions.
Key Applications of Edge Computing Technology
The applications of edge computing span various sectors, enhancing efficiency and driving innovation:
- Smart Cities – In urban environments, edge technology supports real-time data analysis from sensors monitoring traffic, air quality, and public safety. This data allows city planners to make informed decisions and optimize infrastructure.
- Healthcare – In the medical field, edge solutions enable remote patient monitoring by processing data from wearable devices and medical sensors. This allows healthcare providers to respond quickly to changes in patient conditions.
- Manufacturing – Smart factories leverage this technology to gain insights into equipment performance. They can detect anomalies and perform predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and boosting productivity.
- Autonomous Vehicles – Self-driving cars depend on edge computing to process vast amounts of data from sensors and cameras instantly. This capability allows for quick decision-making, ensuring safe navigation.
- Retail – Retailers utilize decentralized processing to analyze customer behavior and inventory levels in real-time. This information facilitates personalized marketing and better stock management.
- Telecommunications – Telecom providers employ edge computing to enhance network performance and reduce latency for applications like video streaming and online gaming. Local processing enables faster, more reliable services for customers.
Challenges of Edge Computing Solutions
While there are many advantages, there are also challenges that organizations must address:
- Deployment Complexity – Implementing these solutions can be complicated, requiring specialized hardware and software. Organizations may need to invest in training and infrastructure to manage these systems effectively.
- Security Concerns – Each edge device represents a potential entry point for cyberattacks. Robust security measures are essential to protect data and prevent vulnerabilities.
- Data Management – Managing and analyzing data at the edge can be challenging due to the volume generated by IoT devices. Effective data management strategies are needed to extract meaningful insights.
- Interoperability Issues – Many organizations use various devices and systems, which can lead to potential interoperability challenges. Ensuring that different solutions work seamlessly together is crucial for maximizing benefits.
- Resource Limitations – Edge devices often have less computing power and storage than centralized servers. Optimizing strategies to balance local processing capabilities with extensive data analysis is essential.

The Future of Decentralized Data Processing
As technology evolves, the future of edge computing looks promising. Here are some trends shaping its development:
- Increased IoT Adoption – With more IoT devices emerging, the demand for edge solutions will grow. Businesses will rely on these systems to manage vast data volumes effectively.
- AI and Machine Learning Integration – Combining edge computing with AI and machine learning will enhance data processing capabilities. This integration will enable advanced analytics and automation at the edge.
- 5G Expansion – The rollout of 5G networks will accelerate the adoption of edge computing. Faster speeds and lower latency will facilitate more devices connecting to edge solutions, enhancing their capabilities.
- Standardization Efforts – As the market matures, standardization will likely increase. Improved interoperability between devices and systems will enhance the effectiveness of edge solutions.
- Focus on Sustainability – With growing environmental concerns, edge computing can contribute to sustainability initiatives. By optimizing data processing and reducing energy consumption, organizations can support green efforts while improving efficiency.
Conclusion
Edge computing represents a significant shift in how data is processed and analyzed. By bringing computation closer to the source, it reduces latency, improves efficiency, and enables real-time decision-making across various applications. As industries continue to embrace this technology, it will play a crucial role in shaping the future of connectivity and innovation.
With its ability to support the growing demands of IoT and other emerging technologies, edge computing is set to transform how we live and work, unlocking new possibilities in our increasingly digital world.
This version reduces the frequency of the keyphrase and varies the subheadings to avoid over-optimization while maintaining clarity and relevance to the topic. Let me know if you need further adjustments!




